Understanding Candida Infection
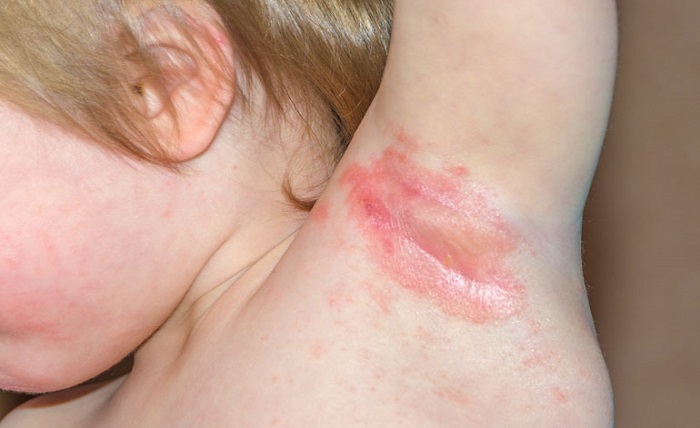
Candida infection, also known as candidiasis or yeast infection, is a common fungal infection caused by the overgrowth of the Candida species, primarily Candida albicans. This infection can affect various parts of the body, including the skin, mouth, throat, genitals, and bloodstream. In this article, we will delve into the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for candida infection.
The symptoms of candida infection can vary depending on the affected area of the body. In oral candidiasis, also known as thrush, individuals may experience white patches on the tongue, inner cheeks, and the roof of the mouth. These patches can be painful and may bleed if scraped. Genital candidiasis, commonly referred to as a yeast infection, can cause itching, burning, and abnormal discharge in both men and women.
Invasive candidiasis occurs when the infection spreads to the bloodstream, leading to potentially life-threatening complications. Symptoms of invasive candidiasis can include fever, chills, low blood pressure, and organ dysfunction.
Causes of Candida Infection
The Candida species naturally resides in the human body, usually in the gastrointestinal tract and on the skin. Under normal circumstances, the body’s immune system keeps the growth of Candida in check. However, certain factors can disrupt this balance, leading to an overgrowth of the fungus and subsequent candida infection.
Common causes of candida infection include a weakened immune system, prolonged use of antibiotics, hormonal changes (such as during pregnancy), uncontrolled diabetes, poor nutrition, and high levels of stress. Additionally, individuals with conditions like HIV/AIDS or those undergoing cancer treatment are more susceptible to developing candida infections.
Treatment of Candida Infection
The treatment of candida infection depends on the severity and location of the infection. For mild cases of oral or genital candidiasis, over-the-counter antifungal medications in the form of creams, ointments, or suppositories can provide relief. However, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
In cases of more severe or recurrent candida infections, prescription antifungal medications may be necessary. These can be administered orally or intravenously, depending on the severity of the infection. Antifungal medications such as daktarin creme, fluconazole, amphotericin B, or echinocandins are commonly prescribed.
In addition to medication, lifestyle changes can play a crucial role in managing candida infections. These may include maintaining good hygiene, wearing loose-fitting clothing, avoiding irritants, practicing safe sex, and adopting a healthy diet with reduced sugar and refined carbohydrate intake.
Conclusion
Candida infection is a common fungal infection that can affect various parts of the body. Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the underlying causes is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. With appropriate medication and lifestyle adjustments, candida infections can be managed effectively, promoting overall health and well-being. If you suspect a candida infection, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional for guidance.




